Registered Investment Advisers (RIAs) must navigate a complex regulatory framework that demands rigorous compliance efforts.
Central to meeting these demands is a well-crafted and dynamic compliance program that reflects a firm’s unique risk profile and operational structure.
For RIAs seeking to stay ahead, having access to investment advisor compliance insights is essential to fostering a culture of compliance and maintaining regulatory integrity.
Why Investment Advisor Compliance Insights Matter Early On
Creating RIA compliance programs relies on accurate, forward-looking knowledge of evolving regulatory expectations.
Early investment advisor compliance perception enables firms to build from the ground up, addressing key areas of risk, operational subtleties, and evolving regulatory expectations.
When knowledge is prioritized in this way, RIAs can build policies, preventative controls, and monitoring workflows that are appropriate to their specific circumstances, as opposed to the generic, one-size-fits-all compliance frameworks that often do not work to preempt enforcement.
Building a Strong RIA Compliance Framework
Creating an effective compliance framework involves several critical components:
1. Written Policies and Procedures
RIAs are required to adopt and implement written policies and procedures relating to compliance with all applicable rules and regulations relating to: portfolio management, disclosures, privacy, best execution, and safeguarding of client funds and securities, and must review and update these policies and procedures as rules change.
2. Appointment of a Chief Compliance Officer (CCO)
The CCO is the foundation of the compliance function.
Accordingly, the CCO should be experienced, appropriately resourced, and vested with sufficient authority to effectively manage and enforce compliance across the firm.
Assigning supervisory controls could ease the process in some situations.
3. Regular Compliance Training
Employees who continue to train remain informed of regulatory changes and internal policies.
For example, they learn about cybersecurity threats, how they document compliance, and how they navigate potential conflicts of interest.
This training commits the whole company to compliance.
4. Monitoring, Surveillance, and Auditing
Internal audits and surveillance aid in identifying suspected violations.
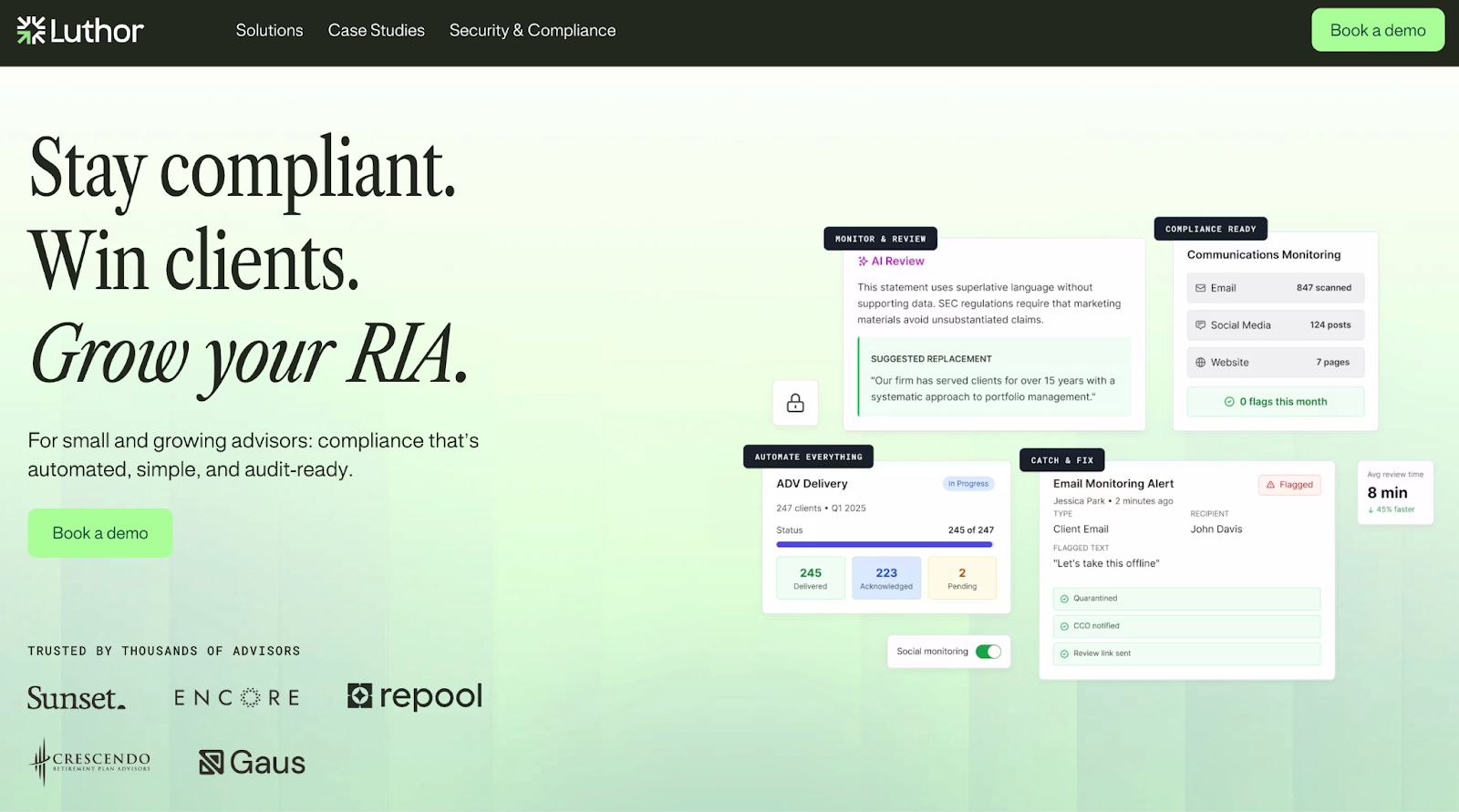
Many modern compliance programs use technology to monitor communications, trading activity, and recordkeeping on a continuing basis.
Scheduled audits are used for assessing controls and processes, to allow time for remediation.

Practical Steps to Maintain Compliance
Implement a Compliance Calendar
To help organize all these deadlines, RIA firms can create a compliance calendar to list when regulatory filings, internal review deadlines, employee training deadlines, and audits are due to proactively ensure timely compliance.
Vendor Management and Due Diligence
As many RIAs give custodial services or technology services to outside firms, assessing third-party providers’ compliance is an important part of a firm’s due diligence effort.
This includes verifying their data privacy and business continuity programs in order to identify whether those programs meet regulatory obligations.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
RIAs should consider adopting endpoint detection and response software, encrypting client information, educating staff on identifying phishing and social-engineering attacks, and periodically reviewing their cybersecurity policies because cyberthreats are increasing.
Importance of Annual Compliance Reviews
An annual in-depth compliance review allows firms to evaluate overall program effectiveness, assess risk areas, and update policies based on regulatory developments and business changes.
These reviews serve as a critical risk mitigation exercise, often involving:
- Thorough examination of advisory agreements and fee structures for adherence,
- Evaluation of marketing and advertising materials for regulatory compliance,
- Cybersecurity readiness assessments,
- Client file inspections to verify suitability and disclosure practices.
Leveraging Technology for Compliance Efficiency
Technology can help firms manage compliance complexity.
Automated alerts, real-time monitoring, and digital audit trails reduce human error, while technology liberates resources for firms to pursue planned compliance.
For example, tools like those from Luthor.ai can ease audits, recordkeeping, regulatory reporting, oversight, and other processes, reducing the administrative burden on financial professionals.
Cultivating a Culture of Compliance
Besides implementing the best controls and processes, an effective compliance program will also impart a culture of compliance by encouraging employees to openly discuss compliance risks, report compliance risks, and update training materials regularly.
Conclusion
RIA compliance needs a strategy.
The strategy must be properly funded.
The strategy must be technology-enabled.
The strategy must consider each advisory firm’s unique business model.
The strategy must consider each advisory firm’s risk profile.
Advisory firms are able to meet regulatory requirements while providing comfort to clients and maintaining continuity of business through developing early perceptions about investment advisor compliance, creating broad and thorough policies and procedures, deploying effective leadership, and utilizing technology.